Learn how to test for bone density and assess your risk of osteoporosis.
How to Test for Bone Density
Bone density is an important aspect of overall health that often goes unnoticed until it becomes a problem. Understanding your bone density can help you take proactive measures to maintain strong and healthy bones. In this article, we will explore the meaning of bone density, the factors that can affect it, the symptoms of low bone density, the different methods available for testing it, and how to interpret the results. So let’s dive right in and uncover the fascinating world of bone density!
Understanding Bone Density
Before we can start testing for bone density, it’s important to grasp what bone density actually means. So, what exactly is bone density? Well, it refers to the amount of mineral content present in your bones. Imagine your bones as a high-rise building, and the mineral content as the sturdy bricks that hold it together. The higher the bone density, the stronger and more resistant your bones are to fractures.
But let’s dive deeper into the fascinating world of bone density. Did you know that bone density is not a fixed value? It can change throughout your life, influenced by various factors such as age, gender, genetics, and lifestyle choices. During childhood and adolescence, bone density increases as the body grows and develops. This is why it’s crucial to build strong bones during these formative years, as they will serve as a foundation for the rest of your life.
What is Bone Density?
Bone density is a measure of how tightly packed the minerals are within your bones. It determines their overall strength and ability to withstand external pressures. Think of it as the superhero shield protecting your bones from breakages and cracks. Now that’s definitely a shield we all want to have!
But what exactly are these minerals that contribute to bone density? The primary mineral is calcium, which is well-known for its role in building strong bones. However, other minerals such as phosphorus, magnesium, and fluoride also play a crucial part in maintaining optimal bone density. These minerals work together like a symphony, ensuring that your bones remain strong and resilient.
Importance of Healthy Bone Density
Adequate bone density is crucial for maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle. After all, who wants to spend their days worrying about fragile bones? Strong bone density not only helps prevent fractures but also lowers the risk of osteoporosis, a condition where bones become weak and brittle. So, by maintaining healthy bone density, you can leap, jump, and dance your way through life without fearing a bone mishap!
Now, let’s talk about some practical ways to improve and maintain healthy bone density. One of the most effective methods is through weight-bearing exercises. Activities like walking, running, dancing, and weightlifting put stress on your bones, stimulating them to become stronger and denser. Additionally, a balanced diet rich in calcium and other essential nutrients is essential for bone health. Foods such as dairy products, leafy greens, nuts, and fish are excellent sources of these bone-loving nutrients.
Furthermore, it’s important to avoid habits that can negatively impact bone density. Excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle can all contribute to decreased bone density over time. So, it’s worth making some lifestyle adjustments to ensure that your bones remain strong and resilient.
In conclusion, bone density is not just a simple measure of mineral content in your bones. It’s a complex and fascinating aspect of your overall health. By understanding the importance of healthy bone density and taking proactive steps to maintain it, you can enjoy a life filled with strength, vitality, and freedom from bone-related worries.
Factors Affecting Bone Density
Several factors can influence your bone density, and it’s important to be aware of them. Let’s take a look at the three main culprits that can either boost or bust your bone density levels.
Age and Bone Density
As the years go by, our bone density tends to decrease. This natural process is known as bone remodeling, where old bone tissue is replaced by new bone tissue. Sadly, this means that we become more prone to bone-related issues as we gracefully age. But fear not! By engaging in regular exercise, consuming calcium-rich foods, and getting enough vitamin D, you can help slow down the bone density decline and keep those bones in tip-top shape!
Regular exercise, such as weight-bearing exercises like walking, running, or weightlifting, helps stimulate bone growth and strengthen the bones. Calcium-rich foods, such as dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified cereals, provide the necessary building blocks for bone formation. Vitamin D, which can be obtained through sunlight exposure or supplements, aids in the absorption of calcium and promotes bone health.
Lifestyle and Bone Density
Our daily habits play a significant role in determining our bone density. Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle can all contribute to lower bone density levels. Smoking, for instance, has been shown to decrease bone density and increase the risk of fractures. Excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb calcium, leading to weaker bones. A sedentary lifestyle, characterized by prolonged sitting or inactivity, can also contribute to bone loss.
So it’s time to kick those bad habits to the curb and embrace a healthy and active lifestyle. Quitting smoking, limiting alcohol intake, and incorporating regular physical activity into your routine can help improve bone density. Weight-bearing exercises, resistance training, and activities that promote balance and coordination, such as yoga or tai chi, are particularly beneficial for bone health.
Genetics and Bone Density
Let’s not forget about our DNA! Genetics also play a role in determining our bone density. If you have a family history of low bone density or osteoporosis, it’s important to be extra vigilant and take proactive measures to maintain healthy bones.
While we can’t change our genetic makeup, we can still take steps to optimize our bone health. Regular exercise and a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D are essential for everyone, regardless of their genetic predisposition. Additionally, consulting with a healthcare professional can help assess your individual risk factors and provide personalized recommendations to support your bone health.
In conclusion, bone density is influenced by various factors, including age, lifestyle choices, and genetics. By understanding these factors and implementing healthy habits, you can take control of your bone health and reduce the risk of bone-related issues. So start prioritizing exercise, nutrition, and overall well-being to keep your bones strong and resilient!
Symptoms of Low Bone Density
Now that we understand what bone density is and what factors can affect it, let’s delve into the symptoms of low bone density. Recognizing the signs can help you take action before things take a tumble.
Low bone density, also known as osteoporosis, is a condition that weakens the bones and makes them more prone to fractures. While it often doesn’t show any specific symptoms until a fracture occurs, there are some common signs that may indicate low bone density.
Recognizing the Signs
One of the most noticeable symptoms of low bone density is frequent bone fractures. These fractures can occur even with minor falls or accidents, and they may take longer to heal than usual. If you find yourself experiencing fractures more often than expected, it could be a sign of low bone density.
Another sign to watch out for is a loss of height. As we age, it’s normal to lose a small amount of height, but if you notice a significant decrease in your height, it could be due to the compression fractures that occur in the spine as a result of low bone density. These fractures can cause the vertebrae to collapse, leading to a noticeable reduction in height.
Back pain is also a common symptom of low bone density. As the bones become weaker, they are less able to support the weight of the body, leading to increased stress on the spine. This can result in chronic back pain that is often worse with movement or prolonged periods of sitting or standing.
If you notice any of these symptoms, don’t brush them off as a mere coincidence – it’s time to get yourself tested! Early detection and treatment of low bone density can help prevent further bone loss and reduce the risk of fractures.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s always better to be safe than sorry, so if you suspect you may have low bone density, it’s wise to seek medical attention. Your healthcare provider can evaluate your symptoms, order the necessary tests, and provide you with the guidance and support you need.
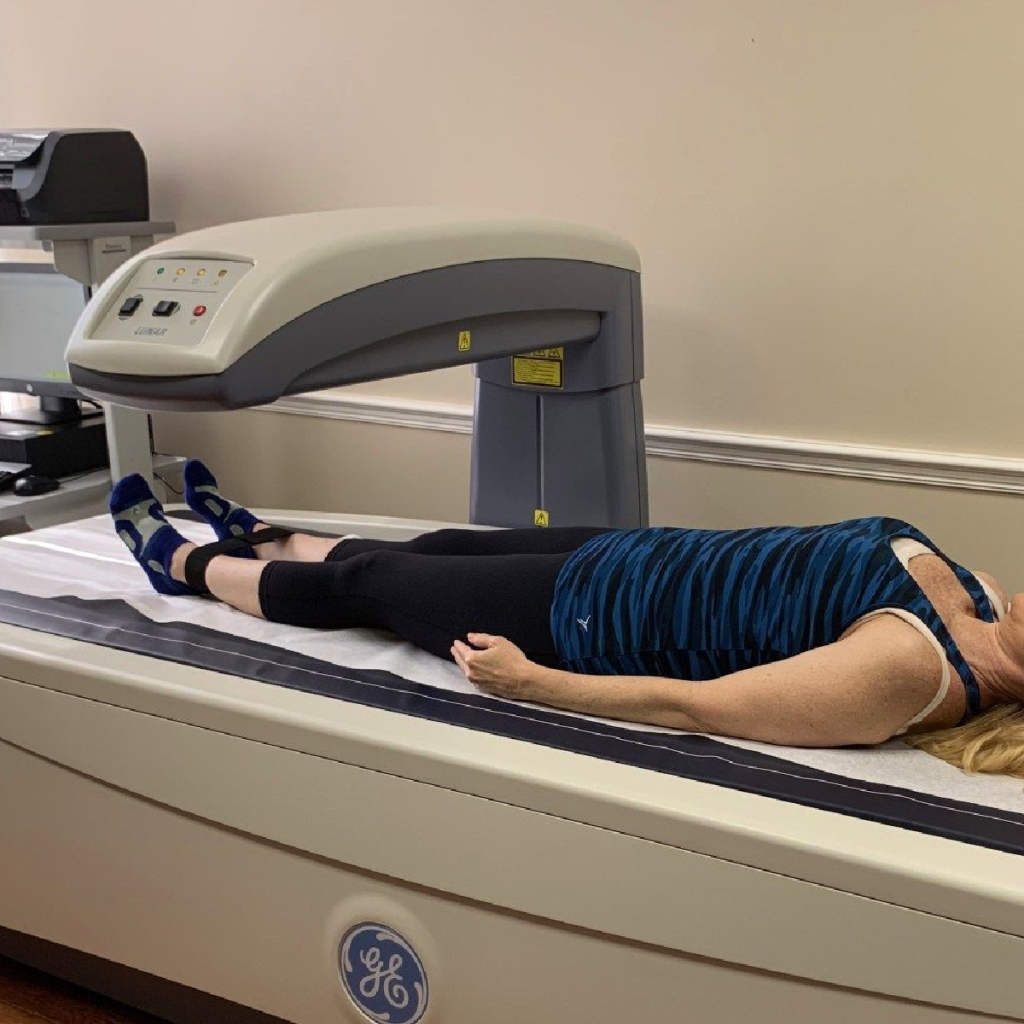
During your medical evaluation, your healthcare provider may perform a bone density test, also known as a DEXA scan, to measure the density of your bones. This painless test uses low-dose X-rays to determine the strength and quality of your bones.
Based on the results of the bone density test and a thorough evaluation of your medical history, your healthcare provider can develop a personalized treatment plan to help improve your bone density and reduce the risk of fractures. This may include lifestyle changes, such as increasing your intake of calcium and vitamin D, engaging in weight-bearing exercises, and possibly medication to help strengthen your bones.
Remember, taking action early is key when it comes to managing low bone density. By recognizing the signs, seeking medical attention, and following your healthcare provider’s recommendations, you can take control of your bone health and reduce the risk of fractures.
Different Methods of Testing Bone Density
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s explore the various methods available for testing bone density. These tests allow healthcare professionals to assess the strength and quality of your bones. Let’s take a closer look:
Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA)
DXA is one of the most commonly used methods for testing bone density. It uses low-level X-rays to measure the mineral content in specific areas of your body, usually the hip and spine. DXA is quick, painless, and provides accurate results, making it a popular choice among healthcare providers.
Quantitative Computed Tomography (QCT)
QCT is a technique that uses computed tomography (CT) scanning to measure bone density. This method is particularly useful for individuals who have metal implants or are overweight, as it can provide more accurate results in such cases.
Peripheral Tests
In addition to DXA and QCT, there are also peripheral tests available to evaluate bone density in peripheral sites such as the wrist, forearm, and heel. These tests are less commonly used but may be recommended in certain situations.
Interpreting Bone Density Test Results
After undergoing a bone density test, you’ll receive a report detailing your results. But what do those numbers really mean? Let’s decode the mystery of T-scores and Z-scores to help you understand your bone density status.

Understanding T-scores and Z-scores
T-scores and Z-scores are used to compare your bone density to that of a healthy young adult. A T-score compares your bone density to that of a young adult of the same sex, while a Z-score compares it to that of someone your own age. Negative scores indicate lower bone density, so the closer you are to zero, the better!
What Your Results Mean for Your Health
Based on your bone density test results, your healthcare provider will assess your risk of fracture and whether any treatment or preventive measures are necessary. So if you’re handed a report with any concerns, don’t fret – it’s all about taking action and keeping your bones strong!
In Conclusion
Understanding and testing for bone density is a crucial step towards maintaining strong and healthy bones. By being aware of the factors that can affect bone density, recognizing the symptoms of low bone density, getting tested using various methods, and interpreting the results, you can take charge of your bone health. So don’t wait until your bones start to creak – empower yourself with knowledge and take action today!







Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?